The grease in the joint is reducing!
There is a problem with the joint space?
You need to replace your joints, it is osteoarthritis.
These are three introductory sentences for osteoarthritis. Every second aged person is a patient for total knee replacement. As per Medicographia Reported published in 2013 in the US alone by 2030 the number of TKR will increase by six times. There is no treatment, as we are told always. But Ayurveda is promising with Osteoarthritis. You can beat and completely treat the osteoarthritis. Certainly, for s particular age and in certain conditions. Here we will try to understand, ayurvedic approach for the treatment of osteoarthritis.
Osteoarthritis is a common condition causing inflammation of joints. It results from the degeneration of cartilage. Because of this, this condition is known as degenerative joint disease. This condition may affect any joint but is more likely to affect the joints that bear most of our weight, such as knees and joints that we use a lot in everyday life such as joints of the hands.

Facts on Osteoarthritis
- Osteoarthritis is the most common type of arthritis.
- It is a long-lasting type of arthritis that features eventual breakdown and loss of the cartilage of one or more joints.
- It affects millions of people across the globe
- Osteoarthritis is also called as wear and tear arthritis.
- The risk of osteoarthritis increases with age.
- In females, osteoarthritis is more common after 55 years of age
- Before 45 years of age, osteoarthritis most frequently affects males.
- Hip osteoarthritis, osteoarthritis of hand and knee osteoarthritis is more common.
- It is one of the leading cause of disability worldwide.
- Most of the people suffer to some degree of osteoarthritis over the age of 60. However, the severity varies.
- People may even suffer from osteoarthritis in there 20’s and 30’s, but there is an underline reason such as joint injury or overuse.
- Unlike other arthritis that are systemic illness, Osteoarthritis does not affect other organs of body except joints.
- Next to ageing obesity is a significant risk factor for osteoarthritis of knees
Symptoms of Osteoarthritis
Joint pain is one thing, we all know. But these symptoms vary from condition to condition. Generally, the symptoms of osteoarthritis develop gradually. It includes:
- Affected joint hurts after a long time of activity or after overuse.
- Sore and aching joints
- Pain with movements
- Loss of flexibility. The patient is unable to move joint through the full range of motion.
- Stiffness in joints after a period of rest. The stiffness is noticeable after being inactive for long or upon waking up.
- Tenderness on applying pressure to or near the affected joint.
- On using the affected joint, the patient may feel grating sensation and might hear crackling or popping.
- Bony enlargement especially at end joints of fingers and in the middle. The bony enlargement may or may not be painful.
- Swelling of joints
- People with osteoarthritis of weight-bearing joints such as knees can develop a limp.
- In osteoarthritis of the cervical spine, osteophytes formed along the arthritis spine that causes pain that radiates from the spine as well as leads to numbness and tingling of the affected part.
- In addition, the symptoms may be intermittent.
The symptoms of osteoarthritis vary from patient to patient. In some patients, symptoms are debilitating, and in others, symptoms may be very few in spite of the dramatic change of the joint that is apparent on X-rays.
Causes of Arthritis
The arthritis is not alone about the age alone. There are many different causes behind this. Depending upon the cause, osteoarthritis is divided into two types:
- Primary or idiopathic osteoarthritis
- Secondary osteoarthritis
Causes of Primary Osteoarthritis
Ageing – Primary osteoarthritis is a part of the natural ageing of our joint in the following steps:
- As we age the water content of the cartilage increases and the protein, makeup degenerates.
- Eventually, the cartilage degenerates forming tiny crevasses or flaking.
- As osteoarthritis advances, there is a total loss of the cartilage cushioning between the joints.
- With the repeated use, the worn joints get inflamed and irritated, leading to pain and swelling.
- Loss of the cartilage cushion results friction between the bones that increases the pain and limits the joint mobility. Inflammation of the cartilage stimulates the outgrowth of new bones around the joint.
- As a combination of all the above factors, the affected joint suffers from a narrowing of the cartilage.
Heredity – Occasionally osteoarthritis may develop in multiple members of the same family.
Causes of Secondary osteoarthritis:
- Obesity – Obesity increases the mechanical stress on the joint and cartilage.
- Repeated trauma – In army military personnel and saucer players repeated trauma to joint is believed to be a leading cause of early osteoarthritis of knees.
- Surgery – Surgery to joint structures
- Abnormal joints at the birth – Some children born with abnormally formed joints are more vulnerable to mechanical wear and tear. This leads to early loss and degeneration of joint cartilage.
- Gout – Gout leads to deposition of uric acid crystals in the cartilage that stimulates degeneration of cartilage and causes osteoarthritis.
- Hormonal disturbance – Hormonal disturbances such as growth hormone disorder, diabetes may lead to early cartilage damage and osteoarthritis.
How Osteoarthritis Occurs
A joint is where the end of two bones come together. Cartilage is a proteins substance that acts as a cushion between joints. It is tough but slippery and smooth tissue. It covers the bone surface and helps in free movement of the bones against each other. The primary function of the cartilage is to reduce the friction between joints. In general, the cartilage can change the shape when compressed and serve as a shock absorber. In patients suffering from osteoarthritis, the cartilage loses elasticity. It becomes thin, stiff, rough and more susceptible to damage. With the time the cartilage loses its ability to act as a shock absorber. As the cartilage deteriorates ligaments and tendons stretch. Joint cannot move as smooth as before and cause of pain. As the condition gets worse, the bone starts rubbing against each other.
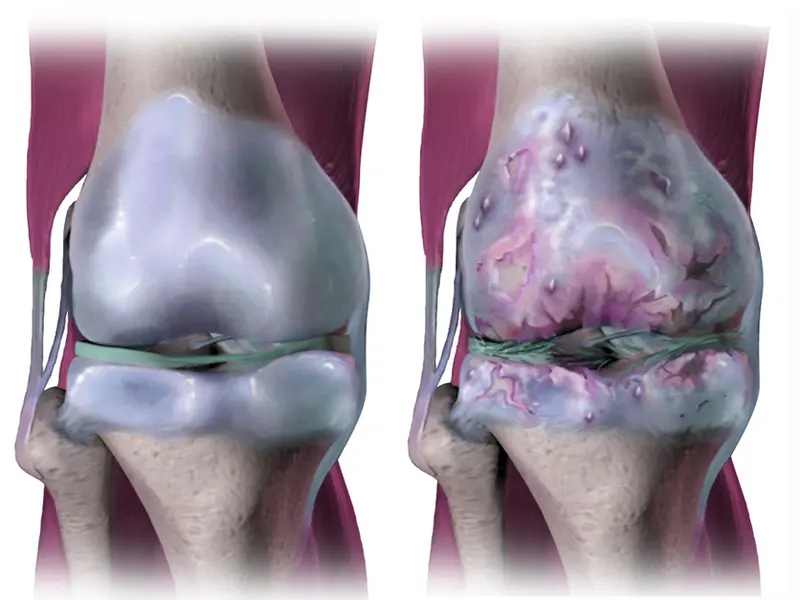
When the cartilage is damaged or worn, the tissues within the joint is overactive to repair the damage. The process of repair changes the structure of the joint so that the joint may work without any stiffness or pain. However, sometimes the repair process fails to work so well and changes to the structure of joint may contribute or become the cause of the symptoms such as swelling pain and difficulty in moving joints properly.
What changes take place in Osteoarthritis in bones
A joint with mild osteoarthritis show the following changes:
- Osteophytes
- Mildly thickened and inflamed synovium
- Thickened and stretched capsule
- Roughened and thinning of cartilage
- A joint formed due to severe osteoarthritis may show the following changes:
- Thickened and crushed up bone little remaining or no cartilage covering.
- Inflamed synovium
- Tight and thickened capsule
- Osteophytes
- Bone deformity
* Osteophytes are extra bone that may form at the joint edge. Sometimes osteophytes rub against other tissues or restrict the movement. At some joints such as finger joint osteophytes are visible as knobbly and firm swelling Aise.
* Synovial is the lining of the joint capsule. Due to the overactive tissues in the join synovium get thickened and produces more fluid the normal which swells the joint.
Ayurveda About Osteoarthritis
Ayurveda considers age as a disease. And age is not about years, as per Ayurveda. This is the wear and tear of the tissues, which decides the age of the human body. Therefore, Ayurveda talks extensively to slow down this process of wear and tear. In the western world, everybody wants to add years in the age, but Ayurveda talks about adding life in the years.
Sandhi Vata
When it comes to the condition of OA, Ayurveda has some similarities with a condition of “Sandhi-Vata”. This is a condition where disturbance of the Vata dosha impacts the joints. While detailing about this condition, Charak writes-
वातपूर्णदृतिस्पर्शः शोथः सन्धिगतेऽनिले |
प्रसारणाकुञ्चनयोः प्रवृत्तिश्च सवेदना ||
The Sanskrit notion translates-
- Cracking sound in joints
- Swelling in Joints.
- Pain while extension and flexion of the joints.
This is the majorly analogised condition with Osteoarthritis.
Asthi Majja Gat Vata
But in the same chapter, Charak talks about another condition and that is- Majja-Asthi-Gat Vata. This is a condition where Vata dosha imbalance is more prominent with Bones and bone marrow- levels of tissues. While discussing the symptoms of this condition, Charak says-
भेदोऽस्थिपर्वणां सन्धिशूलं मांसबलक्षयः |
अस्वप्नः सन्तता रुक् च मज्जास्थिकुपितेऽनिले ||
- Pain as if someone is tearing apart the joints and bones
- Pain in joints
- Muscular devastating.
- Loss of strength in the joints
- Disturbance of sleep
- Regular, severe pain.
These conditions also indicate the condition of OA too.
Today, after spending a lot of money on research and after changing the joints just for money, we know that this is not bone, this is bone marrow which is responsible for the problem of OA. Ayurveda describes it well.
The red bone marrow is something which decides the bone health. And once degenerative changes start appearing in the bones. These changes are more about red bone marrow, then the bone itself. And this is the reason, vitamin D and calcium are not proving helpful for the treatment of OA.
This deep understanding of the condition is the source for the treatment of the condition of osteoarthritis with Dr Pardeep Sharma. He understands the human body with a perspective of Ayurveda therefore he is always helpful in the treatment of these different conditions.
Here is the approach of Ayurveda treatment for OA, which we follow at Sukhayu Ayurved, Jaipur under Dr Pardeep Sharma-
The approach of Ayurveda Treatment for OA
At Sukhayu Ayurved, we do follow a four-dimensional approach for the treatment.
- To stop the further degeneration of the joints and bones
- Regrowing of the bone marrow
- Balancing the fatty part of the bones
- Repairing the damage to the joints
There are specific approaches to achieve these four steps for the treatment of osteoarthritis. Here are the details for these-
To stop the further degeneration of the joints and bones
The right nutrition to the right place is the key to complete health. This same approach we take for the treatment of osteoarthritis. The degeneration cannot be alone about a single Calcium.
Therefore we need to make sure that this nutrition should be proper. And Rasayana therapies are the key to this step. Rasayanas ensures complete nourishment of the body. But this is possible after complete cleansing of the human body.
Regrowing of the bone marrow
As we understand and know that healthy bone marrow is a basic requirement for healthy bones and cartilages. Therefore we work on this aspect through certain Basti Treatments.
Balancing the fatty part of the bones
Ayurveda works on the concept of Gunas. Bones are made up of minerals and calcium. These are dry. Dry things are brittle. When this dryness impacts the bones widely, this condition leads to minor fractures. These minor fractures complicate further.
In scientific words, today we know that the fatty cells are important for healthy bone marrow.
So to achieve these two things, we use certain fats based medicines for healthy bones and joints.
Repairing the damage to the joints
With all the above steps body starts repairing the joints. But to support this healing process is important. And this we do through certain medicines, which are made under guidance of Dr. Pardeep Sharma at Sukhayu only.
This is the approach of treatment we follow at Sukhayu. The ayurvedic line of treatment is also dependant on these steps alone.
Ayurvedic Line of Treatment for Osteoarthritis
We provide the treatment for OA on IPD as well as OPD basis.
- When the condition of the patient is severe, the patient might need to admit in the IPD for extensive panchakarma therapies.
- If the condition of the patient’s joints is not bad, we prescribe certain medicines that patients need to continue back home.
In Panchakarma, generally, we administer –
- Virechana
- Niruha Basti
- Anuvasana Basti
- Lepam and
- Raktamokshana
The selection of these procedures is done according to requirement of the patient.
When you don’t need panchakarma, you just need to come to us for a day where Dr. Sharma will check your joints, your physical condition. After this, our Vaidyas will give you medicines which you need to continue back home.
If you need Panchakarma, you might need to stay with us for 15 days at once.
Everything depends on your condition, your reports, and your requirements.
Ayurvedic Treatment to avoid Knee Replacement
When it comes to osteoarthritis, the most common joints which affect this condition is knee joint. And knee joint replacement is the biggest fear nowadays among elderly people. Therefore the most common question we come across about osteoarthritis of knee joints is-
Can Ayurveda avoid total knee replacement?
And luckily, the answer for this query is affirmative with Sukhayu Ayurved. Yes, you can save your joints and can lead a normal and healthy life. That too without total knee replacement.
Through medicines and panchakarma treatment we can save your joints and can ensure you a healthy and happy life. For the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee joint without surgery, you come to us for consultation or book your video consultation, fill the patient details on the website so that we will contact you regarding this.
Don’t opt for knee replacement. Ayurveda can save your joints.