Have you noticed a purple patch on your skin? Or, do wounds take a long time to clot? Is it possible that your blood has a low platelet count as reported by the blood report? If any of these questions are answered yes, you might be interested in what causes it. We’ll discuss the illness and how we may overcome it with Ayurvedic Treatment. And how does Ayurvedic Treatment for Immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) can help you to lead a normal life?
Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP), also known as Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura, is a blood condition caused by the immune system attacking platelets and resulting in a temporary or continuous decrease in the platelet count and an increased risk of bleeding.
It’s a non-infectious condition.
The word “idiopathic,” which was formerly the name of the condition, means “of unknown origin.” It was utilized in the past because scientists were not yet aware of ITP’s cause. However, research has now shown that the immune system plays a significant role in its development, thus it is now known as immune thrombocytopenia.
What is ITP
Now Let’s break down the term thrombocytopenia, the word “Thrombocytes” are your platelets, and “penia” means you don’t have enough of something. Put those terms together, and you get “thrombocytopenia.”
Since the disorder is based on platelets, I’ll start by discussing them.
A blood cell often referred to as a hematopoietic cell, hemocyte, or hematocyte, is a type of cell formed during hematopoiesis that can be found in the blood. Erythrocytes, leukocytes (white blood cells), and thrombocytes are the three main types of blood cells. By percentage, red blood cells make up 45% of the volume of blood, with plasma making up the remaining 55%.
Platelets, unlike red and white blood cells, are not actual cells but rather tiny pieces of cells. Platelets gather at the site of an injury, adhere to the injured blood vessel’s lining, and form a platform on which blood coagulation may take place by helping with the blood clotting process (or coagulation).
As a result, a blood clot forms over the wound and seals it off from bleeding. Fibrin also serves as the foundation for new tissue development by forming the initial scaffolding.
We will here discuss Ayurvedic Treatment for Immune thrombocytopenia.
Low platlates: the cayse of ITP

The normal range for platelet concentration is 150,000 to 450,000 per cubic millimeter. Internal bleeding or subcutaneous bleeding can occur if the number of platelets is too low (either due to decreased production or increased destruction).
People with ITP often have many purple bruises called purpura on the skin or mucous membranes inside the mouth. These bruises may also appear as pinpoint-sized red or purple dots on the skin called petechiae. Petechiae often look like a rash.
In ITP, the immune system produces antibodies against platelets. These platelets are marked for destruction and removal by the spleen, which lowers the platelet count. The immune system also appears to interfere with cells responsible for normal platelet production, which can further lower the number of platelets in the bloodstream.
Children may develop ITP after a viral infection and usually recover fully without treatment. In adults, the disorder is often long-term.
Types of ITP
The two main types of ITP are acute (short term) and chronic (long term).
Acute Thrombocytopenic Purpura
Acute ITP is the most common form of the disorder and usually occurs spontaneously. Symptoms typically develop within a few days to several weeks after the onset of the illness. The platelet count usually falls rapidly and reaches a nadir (lowest point) within 1 to 2 weeks. After reaching the nadir, the platelet count typically begins to increase gradually and returns to normal within 4 to 6 weeks. However, some people with acute ITP may have a more prolonged course, with a platelet count that does not return to normal or that fluctuates over time.
- Acute ITP is the most common form of ITP. Most commonly seen in young children (ages two to six years).
- Characteristics of acute ITP include:
- Symptoms that follow a viral illness, such as chickenpox.
- Very sudden onset.
- Symptoms that disappear in less than six months (often within a few weeks).
- There is no requirement of the treatment in such conditions. Because it settles down itself with in no time and doesn’t reappear.
Chronic Thrombocytopenic Purpura
Chronic ITP is less common than acute ITP and occurs in about 10% of people. It can be either spontaneous or secondary to a chronic illness or medication use. In children, it most often occurs as a secondary condition in association with common viral illnesses such as chickenpox, flu, and mononucleosis. In children, with exposer to the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), this type of ITP might be related to EBV infection. Secondary ITP is more common in adults than in children and tends to occur after several months following an acute illness or viral infection with EBV.
In secondary chronic ITP, the platelet count falls gradually over time and does not increase despite treatment initially given for acute ITP. The disorder may persist for years without causing serious health problems unless the person has a bleeding episode caused by an injury or surgery.
- Adults have this type of ITP more often than children, but it does affect adolescents.
- Characteristics of chronic ITP include:
- The disorder can happen at any age.
- Symptoms can last a minimum of six months, several years or even a lifetime and treatment is a necessity here.
- Women develop it two to three times more often than men.
When it comes to Ayurvedic Treatment for Immune thrombocytopenia we focus more on this type of ITP.
Symptoms of ITP
Symptoms of ITP generally, include:
- Bruising, especially around the eyes and mouth.
- Purple blotches (purpura) on the skin.
- Pinpoint-sized red or purple dots called petechiae, which may look like a rash.
- Bleeding from the gums, nose, or intestines.
- Unusual tiredness (fatigue).
- Bone pain.
- Swollen lymph nodes.
ITP is a blood disorder that results in a low number of platelets in the bloodstream. Platelets are important for proper blood clotting and without them, patients can suffer from easy bruising and excessive bleeding. ITP was first described in the early 1900s but was not well understood at that time. ITP was only recognized as a distinct disorder in the ’60s.
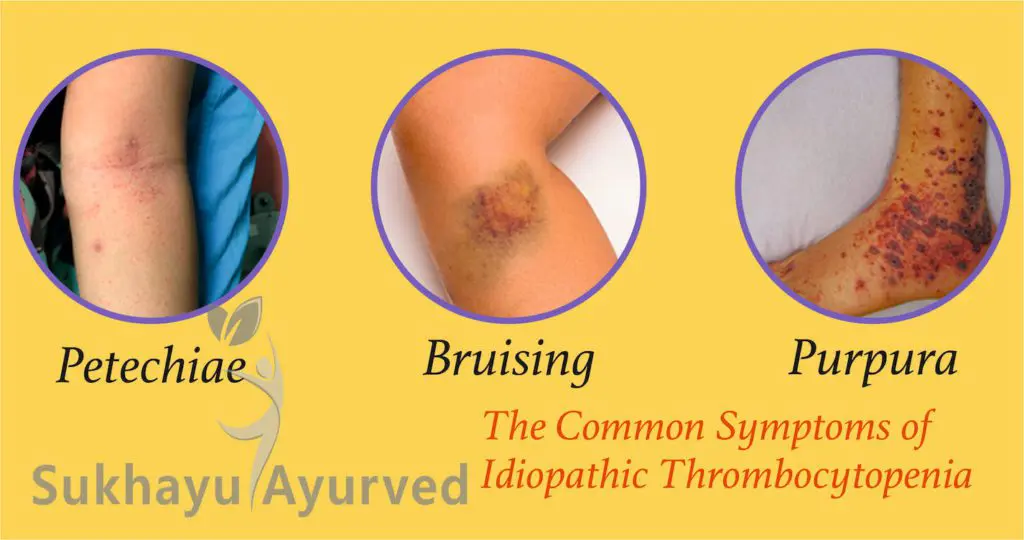
Symptoms of ITP are varied but can include bruising, nosebleeds, bleeding gums, bleeding from the vagina or rectum, blood spots under the skin (petechiae), and fatigue. Some patients may also report bone pain or abdominal pain due to gastrointestinal hemorrhage. Symptoms tend to persist for several days before subsiding completely. Other types of autoimmune disorders are more common among people who have ITP including thyroiditis, rheumatoid arthritis, lupus erythematosus, ulcerative colitis and vasculitides.
Treatment of Idiopathic Thrombocytopenia
Modern medicine treatment for ITP suggests the use of steroids or other similar medications increase platelet count, even though this may help in treating ITP, steroids have a negative impact on our immune system i.e they suppress the immune system, reducing the activation/efficacy of it, this leaves our body vulnerable to other diseases.
Complications of ITP treatment
The treatments for ITP can have more risks than the disease itself. The long-term use of steroids dominated medication can cause serious side effects, including:
- osteoporosis
- cataracts
- a loss of muscle mass
- an increased risk of infection
- Diabetes
Other general complications include
- fatigue
- nausea
- headaches
- Fever and chills
Ayurveda About Idiopathic Thrombocytopaenia
Ayurveda is one of the oldest and most holistic systems of medicine in the world. It is a 5000-year-old tradition that aims to restore balance within the body, mind, and spirit. Ayurveda recognizes that all illness arises from an imbalance within the body, and takes a whole-body approach to treatment. ITP has a proper cure with Ayurvedic treatment.
In Ayurveda, ITP is known as “rakta pitta” or “rakta shotha.” It is considered to be a blood disorder that results in the abnormal destruction of platelets. This can lead to a decrease in the number of platelets in the blood, which can cause excessive bleeding. ITP is a relatively rare condition, and the cause is unknown in most cases. However, there are a number of potential causes, including autoimmune disorders, infections, and certain medications.
Ayurveda treats ITP with Herbal medicines and Panchakarma Treatment which is a unique therapy to cleanse the body of toxins, improve blood circulation, boost energy levels, promote overall health & wellbeing.
Panchakarma in ancient Indian medicine means ‘five actions”. It is a process of cleansing done for the physical, mental and spiritual well-being. It includes 5 processes viz- Snehana (Oleation), Swedana (Sweating), Virechana (purgation), Basti (Medicated Enema). Through these processes, ITP can be cured, when planned properly.
Ayurveda: A ray of hope for ITP
Ayurveda is a complete system of medicine that not only cures the disease but also helps in preventing its recurrence. It is a natural, safe and gentle system of medicine that can be used by people of all ages. It is especially beneficial for those who want to maintain their health and prevent diseases from occurring.
Ayurveda is an ancient and holistic system of medicine that can treat ITP effectively. Panchakarma therapy is a unique cleansing process that helps to restore balance within the body and improve overall health and wellbeing. Ayurveda is a safe and gentle system of medicine that helps people of all ages to maintain their health and prevent the disease from occurring. Many diseases which are incurable with a contemporary system of medicine are curable with Ayurveda. Consult Vaidya Pardeep Sharma for better treatment of your condition.
Ayurvedic cure for Mix Connective Tissue Disorder
Ayurvedic Treatment for Immune thrombocytopenia
One of the major functions of bone marrow is the production of platelets and since the main cause of ITP is decreased production of platelets we can conclude that majjagata vatavyadhi (vitiated vata residing in bone marrow) leads to ITP.
ITP is a result of vitiation of Vata and majja, this implies that to treat ITP we have to treat both these issues.
- Causative factors for Vata vitiation
- Having a diet that consists of dry, cold food
- Excessive fasting
- Excessive Swimming, exercise, or any other physical activities in excess
- Suppression of natural urges
The above-mentioned factors vitiate Vata Doshas. This aggravated Vata impacts the bone marrow. Because Vata is naturally inhabitated in the bone marrow.
Because it is already upset due to factors like consumption of incompatible food combinations (pizza with coke, citrus fruits with milk, etc). Hence it is advisable to avoid such a diet or consume in very limited proportions. Such eating habits lead to vitiated pitta in the body which is a compatible element with blood results in vitiating the blood too. This phenomenon aggravates the ITP.
Majja is one of the seven dhatus. Unhealthy and incompatible foods have become an inseparable part of the modern lifestyle, this type of diet leads to various health issues. Such a diet interferes with the metabolism of Dhatus, which obstructs the process of development of Dhatus and causes diseases of different nature. Majja also disturbs with such a diet. Hence bone marrow is unable to produce an optimal count of platelets leading to ITP.
The same approach we follow for the Ayurvedic Treatment for Immune thrombocytopenia.
Does Ayurveda believe in increasing immunity?
Ayurvedic Line of treatment for ITP
Ayurveda provides a fundamental solution to this problem. Both Vata and Majja can be treated with the use of PanchaKarma. Ayurveda helps in alleviating the root cause along with cellular detoxification. This is the most prominent reason due to which people across the globe have huge faith in Ayurvedic medicines and therapies.
Treatment of the disease consists of avoiding causative factors responsible for disequilibrium of the body matrix or of any of its constituent parts through the use of Panchakarma procedures, medicines, suitable diet, activity, and regimen for restoring the balance and strengthening the body mechanisms to prevent or minimize future occurrence of the disease with Ayurvedic Treatment for Immune thrombocytopenia.
General Precautions
- Avoid certain over-the-counter drugs that can affect platelet function, including aspirin, ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin), and the blood-thinning medication warfarin (Coumadin).
- Limit your intake of alcohol because consuming alcohol can adversely affect blood clotting.
- Choose low-impact activities instead of competitive sports or other high-impact activities to decrease your risk of injury and bleeding.
- Eat a varied, well-balanced diet that includes healthy foods like lean meat, vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and low-fat dairy products.
- Maintain ideal body weight. Research has shown that obesity can contribute to platelets clumping together. Those who are overweight or obese may be at increased risk of ITP due to the additional demands placed on the bone marrow.